Autoimmune diseases are conditions in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and a range of symptoms. While there is no cure for autoimmune diseases, managing symptoms and flare-ups can be achieved through various treatments, including medication, lifestyle changes, and diet.
Understanding the Impact of Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in managing autoimmune diseases as certain foods can either trigger inflammation or help reduce it. A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can help support the immune system and reduce inflammation, while processed foods, sugar, and trans fats can exacerbate symptoms.
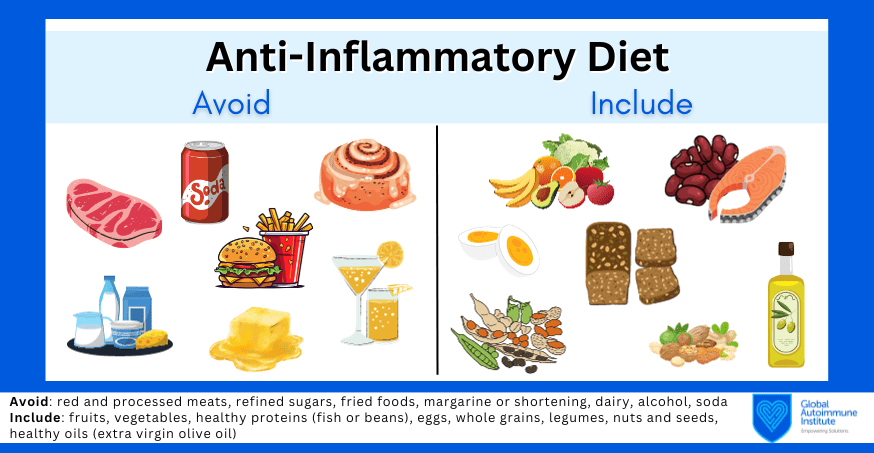
The Importance of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet is key in managing autoimmune diseases as it focuses on reducing inflammation in the body. This type of diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats such as omega-3 fatty acids. Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, can help combat inflammation and support the immune system.
Key Nutrients for Managing Autoimmune Diseases
Certain nutrients play a crucial role in managing autoimmune diseases, including vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and probiotics. Vitamin D helps regulate the immune system and reduce inflammation, while omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish and flaxseeds can help reduce inflammation. Probiotics, found in fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi, can help support gut health and reduce inflammation.
Common Triggers to Avoid
Certain foods can trigger inflammation and exacerbate symptoms of autoimmune diseases. Common triggers to avoid include processed foods, sugar, gluten, dairy, and artificial additives. It’s important to listen to your body and identify which foods worsen your symptoms, as everyone’s triggers can vary.
Creating a Personalized Approach
Managing autoimmune diseases through diet is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to create a personalized plan that fits your individual needs and preferences. Keep a food diary to track how certain foods affect your symptoms and make adjustments accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diet plays a crucial role in managing autoimmune diseases by reducing inflammation and supporting the immune system. An anti-inflammatory diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health. By avoiding common triggers and focusing on key nutrients, individuals with autoimmune diseases can take control of their health and well-being through the power of food. Remember to consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to create a personalized plan that works best for you.